I am highlighting this statement from the Ministry of Education and Child Care because this cannot be talked about and screamed from the roof tops enough.
I am highlighting this statement from the Ministry of Education and Child Care because this cannot be talked about and screamed from the roof tops enough.

Acronyms are often used in social media posts, emails and chatter amongst parents/guardians and school district professionals. I personally feel there are so many of them and they are constantly changing. Sometimes it’s just hard to keep up! Districts also don’t always use the same language for their education roles. More confusion.
Here is a list compiled by over 30 parents from different districts across British Columbia, to help new parents who are entering the world of education advocacy. Or, even if you aren’t new, here is a list, because who can always keep track of these things??
If you want to add any, please email me.
These acronyms have not made it on the list because I have critiqued or placed judgement on these terms, they are simply acronyms you might come across.
If you are a parent/guardian attending meetings or are receiving communication and people are tossing around acronyms/terms/language you don’t understand, you have every right to stop them and ask them to explain. Jargon can create barriers in communication. We all have the right to understand what people are talking about when it concerns us and our children.
In addition to the acronym list below, here is also a Glossary of Terms from the BC Government for K-12 Education.
(Updated September 14th, 2022. Now over 40 parents contributed. 🙂 )
CB IEP – Competency Based Individual Education Plan
IEP – Individualized Education Plan
SLP – Student Learning Plan
SD – School District
ID – Image Description
TW – Trigger Warning
Specialized Professionals
AAC SLP – Alternative Augmentative Communication Speech Language Pathologist
BC – Behavioural Consultant
BCBA-Board Certified Behaviour Consultant
BI – Behavioural Interventionist
OT– Occupational Therapist
PT– Physiotherapist
SLP – Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP can also be Student Learning Plan)
SW – Social Worker
Support Roles/Teams/Job Titles in Education
ASW – Autism Support Worker
BSW – Behavioural Assistance Worker
CM – Case Manager
CRT—Classroom Teacher
DIMT – District Inclusion Mentor Teacher
DLT – District Leadership Team
EA – Education Assistant
IST– Integration Support Teacher AND/ Inclusion Support Teacher
ITT– Inclusive Team Teacher
LAW – Learning Assistance Worker
LRT – Learning Resource Teacher
LST – Learning Services Teacher AND/ Learning Support Teacher
RT – Resource Teacher
SBT – School-Based Team
SEA – Special Education Assistant
SERT – Special Education Resource Teacher
TTOC – Teaching Teacher On Call
YCW – Youth Care Worker
Organizations
AFU – Autism Funding Unit
ASNBC – Autism Support Network BC
BCCDC – BC Centre for Disease Control
BCCH – BC (British Columbia) Children’s Hospital
BCTF – BC Teacher’s Federation
CADDRA – Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance
CAN – Canucks Autism Network
CLBC – Community Living BC
CYMH – Child & Youth Mental Health, Government of BC
CUPE – Canadian Union of Public Employees
DPAC – District Parent Advisory Council
FSI – Family Support Institute
KMH / KMHRC / Kelty – Kelty Mental Health Resource Centre
MCFD – Ministry of Child and Family Development
MOECC – Ministry of Education and Child Care
MOH – Ministry of Health
P1/P2 – BCCH Child Psychiatry Inpatient/Outpatient Units
PAC – Parent Advisory Council
PAFN – Pacific Autism Family Network
POPARD – Provincial Outreach for Autism and Related Disorder
SET BC – Special Education Technology British Columbia
Administrative Processes
FOI – Freedom of Information Request
HR – Human Resources
HRT – Human Rights Tribunal
OIPC – Office of Information Privacy Commissioner
TRB – Teacher’s Regulation Branch
Loosely Grouped
DX – Diagnosis
IFL-identify first language
PFL-person first language
ND – Neurodivergent / Neurodiversity
NT – Neurotypical
PWD – Person With a Disability
ABA – Applied Behavioural Analysis
ACC – Augmentative Assistant Communication
AT– Assistive Technology
B&M – Brick and Mortar School (A physical building where students attend)
CBT – Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
CPI – Crisis Prevention Intervention
DL – Distance Learning
DSM-5 – Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Health Disorders (5th Ed.)
FI – French Immersion
FSA – Foundation Skills Assessment
HS – Home Schooling
IQ – Intelligence Quotient
ISP – Inclusion Support Program
LS – Life Skills
LSS – Learning Support Services
NSS-Nursing Support Services
OL – Online Learning
Psych Ed – Psycho-Educational Assessment
SE – Supportive Education
SEL – Social Emotional Learning
SPED – Special Education
TIP – Trauma-Informed Practice
UDL – Universal Design for Learning
EAL – English as Another Language
ELL – English Language Learner
ELL – English Language Workers
ESL – English as a Second Language
2E – Twice Exceptional
AS – Autism Spectrum
ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
CAPD – Central Auditory Processing Disorder
CNP – Complex Neuropsychiatric Profile
CP – Cerebral Palsy
DCD – Developmental Coordination Disorder
DD– Developmental Disability
DS – Down Syndrome
GAD – Generalized Anxiety Disorder
FASD – Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
HH – Hard of Hearing
ID – Intellectual Disability
LD – Learning Disability
OCD – Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
ODD – Oppositional Defiance Disorder
PD– Physical Disability
PDA – Pervasive Drive for Autonomy (Pervasive Demand Avoidance)
SCD – Social Communication Disorder
SPD – Sensory Processing Disorder
VI – Visually Impaired
Designation Categories
A – Physically Dependent
B – DeafBlind
C – Students with Moderate to Profound Intellectual Disabilities
D – Physical Disabilities or Chronic Health Impairments
E – Visual Impairments
F – Deaf or Hard of Hearing
G – Autism Spectrum Disorder
H – Students Requiring Intensive Behaviour Intervention or Students with Serious Mental Illness
K – Students with Mild Intellectual Disabilities
P – Gifted
Q – Learning Disabilities
R – Students Requiring Moderate Behaviour Support or Students with Mental Illness
Page 3:

This is a look at whether the Commissioner errored in law and how it was applied. Not about the actual decision.
A Human Rights Lawyer told me that Judicial reviews are very risky as very rarely do the complainants win. The respondents can and will apply for costs to have their legal fees paid for. You as the parent will then need to pay. Legal fees can be tens of thousands of dollars.
I HIGHLY encourage parents/guardians who are considering this route to consult with a lawyer. The $500 you spend on a consultation fee may save you thousands of dollars in the end.
4. Next option is Ombudsperson BC. The chances of them conducting a review are very slim. Please email me if you would like more details or tips or how to get your case at least to an investigator. Ombudsperson will also not look at the decision, but looks at the process. They track every attempt at a complaint, so even it yours doesn’t make it to an investigator, your intake form alone is helping. Your arguments to them are going to need to be grounded in administrative fairness.

I have asked the Ombudsperson separate the TRB from the Ministry of Education in their annual data reports, so we can track how many people are filing complaints against the TRB, as they refused to disclose this information in a Freedom of Information request. They seemed receptive to the idea, so I’ll be watching their annual report coming out this to year to see if my request was accepted. If not, I’ll follow up.

5. Right now, if someone asked me what they could do with decision letters that they know are not right. I would tell them, to please consider filing with Ombudsperson and go through the process, even if the chances of success are slim. We need to let them know that we are not satisfied with the TRB and Ombudsperson determines what needs are out there, based on whether people are filing complaints or not. So, your voice on this does matter.
Please consider providing feedback to the Ministry of Education.
Also, please consider contacting me. There is a wider much larger project that I am working on, and I would love to hear other people’s stories.
6. Getting your complaint to a consent resolution is slim. Right now the most recent stats from the Commissioner’s office reveals that from April – June, only 7% made it to a consent resolution.
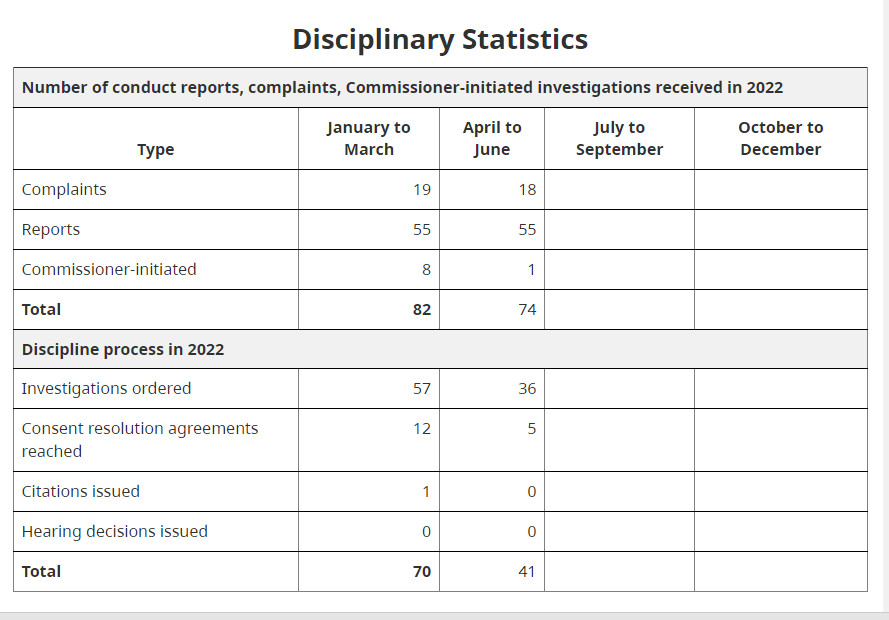
It sounds like a dead end. What’s the point? Here it is. When we file complaints they stay on the certificate holder’s record. If there is more than one complaint and they build, the chance of success increase. You are basically filing to help out the next parent or the next child. And, who knows…maybe this isn’t the first time that someone has filed a complaint and yours will actually be successful.
If we say nothing and don’t speak up, it helps no one. It’s like it never even happened. Don’t get your hopes up. Manage expectations, but file with the TRB, and then file with Ombudsperson. Oh and then call me and blab all about it. I’ll make your effort worth it. You’ll be part of a larger story. 😉
Hello Parents.
Welcome to advocacy summer camp. You have two months to get in advocacy shape for the upcoming school year in the fall. Well….technically you don’t have two months, advocacy is a life long learning journey, but it’s more of a reflection of the sense of urgency we all feel when our kids are struggling.
If you are new to advocacy and are wondering where in the world to start, here is your summer reading.
Let’s start here. With information. The more you know, the better you will be at advocating for your child.
Start with Your District Website
District websites can be a maze. A complete maze. Keep going.
Look at Provincial Manuals and Acts
Legal Cases in Education
What are my External Organization options?
Where Can I go for Advocacy Help?
What about the Process of Advocacy?
This page was last updated on July 21, 2022.
IF anyone has any more information of manuals that they feel belong on this list, please email me and I will update it.
Here are some interesting stats I have looked at, see below.
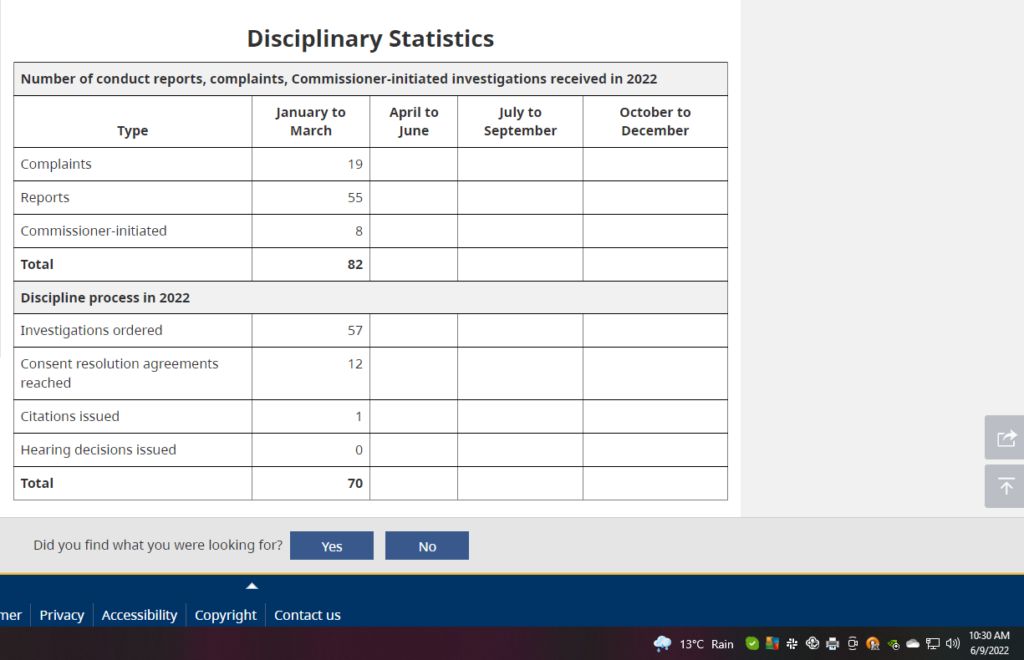
For Jan to March 2022, only 14% reached consent resolution stage.
In the past year I have looked at all of the discipline reports for consent resolutions. Here is the conclusion:
Reports of sexual nature: 10
Reports of risk/harm of physical safety: 7
Reports of negative emotional experiences: 5
Of those 5 involving social/emotional experiences
1- teacher disciplined for Facebook post
1 – teacher had multiple offences of similar behaviour
1 – report made by the district
2 teachers were disciplined for showing inappropriate material in the classroom
I have so much to say on this topic, but I’ll have to save most of it for later. ![]() Just wanted to give you all some info. If you are making a complaint, it will help if you can tie it to some sort of physical risk. Also note that the Commissioner is going to be looking for a “marked departure” from the teacher’s standards. He uses the Teacher’s Act as the guide for the administrative tribunal process. He needs to believe that if it went in front of a hearing panel that they would all see a “marked departure” from the standards.
Just wanted to give you all some info. If you are making a complaint, it will help if you can tie it to some sort of physical risk. Also note that the Commissioner is going to be looking for a “marked departure” from the teacher’s standards. He uses the Teacher’s Act as the guide for the administrative tribunal process. He needs to believe that if it went in front of a hearing panel that they would all see a “marked departure” from the standards.
Even if your complaint doesn’t reach any consent resolution it is kept on the file of that teacher. So if there is a repeat of behaviour, it will probably help another parent who is in the position of also having to make a complaint.
Reports from the district seem to be MOST successful. If you have serious concerns about a teacher, one resolution could be that the district agrees to write a report to the TRB. That will more likely make it through than coming from a parent. Also note, that if you have serious concerns about a teacher and the superintendent doesn’t inform the TRB, that is an offence in the School Act against that Superintendent.
Can the Attorney General intervene with the Ministry of Education over Wilful Blindness??
Legal term – Wilful Blindness: “The Supreme Court of Canada held that wilful blindness is best described as “deliberate ignorance” and emphasized that it should be treated as a state of mind that is equivalent to actual knowledge.” & “Wilful blindness…involves no departure from the subjective inquiry into the accused’s state of mind which must be undertaken to establish an aider or abettor’s knowledge.” (Verdon-Jones S, 2020, p.98)
I emailed the Ministry of Education and their Legislation department on October 27th, 2021 and informed them of a gap in their legislation connected to counselling notes, and an order from the OIPC (Office of Information Privacy Commissioner) and the upheld decision of such an order by the BC Supreme Court.
I have blogged about it.
The Ministry of Education ignored my multiple emails and my attempts at communication. I filed an Ombudsperson complaint in early December, which forced them to communicate with me and on March 7th, 2022 we finally had a conversation. They acknowledged the gap in the system. They have been aware for 7 months and so far…I haven’t seen or heard of any changes. The Board of Education has also been aware since October 26th, 2021 and I have not seen or know about any attempts at updating policy to reflect case law, which the Ministry of Education states is their responsibility. They are also ignoring my emails regarding this topic.
Due to a Freedom of Information request and a phone call with the finance department it was revealed that the Ministry of Education isn’t tracking human rights violation financial data that are occurring across the province. The Freedom of Information on the financial implications of such complaints had to come from the Ministry of Finance. Talk about deliberate ignorance. I have also written a blog about this topic.
I have emailed the Ministry of Education, the Executive Director of the TRB and the Commissioner. I have raised serious issues regarding their process and their legislation and the connection with Ombudsperson. They refuse to respond or discuss these issues. I am not telling them their welcome mat is crooked, I am telling them their house is on fire. They undemocratically responded by closing the door. There will be an upcoming blog about this. It’s been over a year and processes are still occurring with Ombudsperson regarding these issues. More to come about this later. Last year I blogged about a call for fair process. Since then, the story gets deeper. For those who need some inside tips on the process, here you go.
When I presented the Ministry of Education with a document containing evidence of my allegations of educational malpractice, they referred me to Ombudsperson and the Teacher’s Regulation Branch. Both due to systemic and legislative reasons were dead ends. When I went back to them, they apologized and said there was nothing they could do. It turns out there are no avenues for accountability in the education system regarding educational malpractice. Nothing.
What are we supposed to do when we have a government body refusing to uphold case law, deliberating ignoring human rights violations, closing the door of any conversation related to systemic oppression, and having no accountability system for allegations of malpractice?
Anyone have any ideas?????
I’d love to hear them.
Seriously.
*****************
References
Verdon-Jones, Simon N. (2020). Criminal law in Canada: Cases, questions, and the code. (7th edition). Top Hat.
Friday May 20th, I submitted a Freedom of Information request to Ombudsperson BC requesting the following information.
“I would like data of the past 10 years, (May 2012- May 2022) of how many parents have submitted complaints with the Teacher’s Regulation Branch, and how many of those complaints were investigated by an investigator. Please separate the data by year.”
Today, May 25th my request was denied. In a letter from the Deputy of Ombudsperson it was explained to me that FIPPA has very limited access to Ombudsperson due to that they are an office of the Legislature and I can only access information they post publicly. They recommended I look at their annual reports.
SO……
I went through all of their authority statistics reports. I can’t get any information specific on the Professional Conduct Unit (formerly Teacher’s Regulation Branch), only under the Ministry of Education. Based on the information in their authority statistic reports, I have created a graph for easy consumption.
This graph depicts the number of files Ombudsperson opened connected to the Ministry of Education from 2011-March2011. Data for this previous year will be posted on the Ombudsperson website in a month or two.
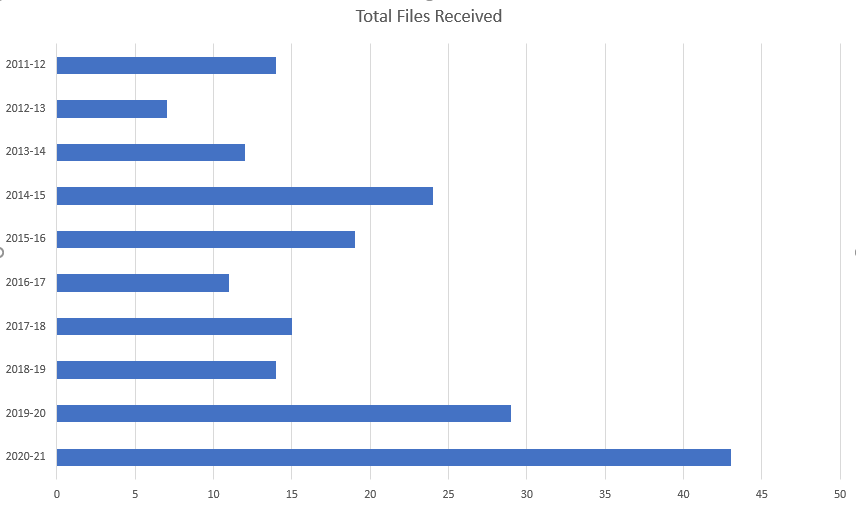
Here is a table version of the same data.
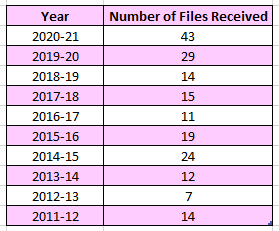
I find their annual reports and authority statistics reports to be very interesting. I highly encourage people who are interested in human systems, data and social justice to take a look.
For each file that was opened, you need to be so frustrated with your situation that you are filing a complaint with Ombudsperson, and be willing to wait months for something to be resolved…or not.
I have recently submitted an FOI request through the Ministry of Education requesting very similar and more detailed information. I will keep you all posted.
Also, keep in mind the the Ministry of Education is not tracking any Human Rights Complaint data. As I have blogged about previously, through another FOI request result.
When a teacher daily allows a student with a learning disability to fail their class, but does not even lift a finger to inform the case manager or parent, that is ableism and its discrimination. Disabled children failing, falling behind and being excluded without accommodations have become the normality of the education system. It’s so common, it is woven into the fabrics of the system.
They just invisibly slip through the cracks, while a detailed IEP sits in a student database system collecting digital dust.
The fact that the Ministry of Education intentionally doesn’t even track information regarding the human rights violations that are occurring across the province is an example of ableism. Disability issues don’t affect them, so they have the privilege to ignore it. Want to know how to systemically keep a marginalized group of people oppressed? Keep them off your radar to begin with. OH…and by the way…the group the people the Ministry of Education are intentionally oppressing, are disabled CHILDREN and their family unit.
What is even more profound is that these teachers who are discriminating are caring people. They love teaching and are inspired by the creations of their students. We think ableist teachers are lurking somewhere in the dark with DON’T CARE tattooed on them, when in fact that simply isn’t the case. When children are ignored and neglected in the education system by good teachers, that is obvious discrimination at its finest. The “other” students get their gifts, and the disabled students get left alone, left behind, and just….left. There are lovely people out there in the world completely unaware of their own biases and the normality of disabled children failing, just blends in with the wall paper. It’s not even a big thing. It’s just something that happens. Shrug.
This is very common in the education system, and the ableism these kids experience is then internalized, becomes part of their self-concept, self-esteem and identity. Want to know why kids turn to drugs and crime? Failure in the education system has been proven to be foundational in many of the peer reviewed journal articles. IT’s not that we do not know. It’s not that more studies are need to be done. We have all the information. Government is just biased, ableist and discriminatory and this shows in their government run and funded education system. It oozes out of the pores of all 60 school districts. It’s not obvious to the people who are not impacted by it. You need to look at the system and not just focus on what is there, but what is missing. Who is missing?
We need to flip this education system upside down and inside out. The future of their lives and our society depends on it.
Ministry of Education- It is time for anti-ableism leadership from your government.
Are we on your radar? Or will we continually be swept under the rug?
I have added a new page under Education Advocacy and this it it!
These are some of the cases and reports that have crossed my path. This is not a list of the ONLY cases. To search for cases go to CANLII
For step by step instructions on HOW to search click HERE and scroll to the lower part of the page.
REPORTS
Advocacy Fatigue: Self-care, Protest, and Education Equity 2015 CanLIIDocs 212
CASES – In BC and across Canada
Moore v. British Columbia (Education), 2012 SCC 61 (CanLII), [2012] 3 SCR 360
Hewko v. B.C., 2006 BCSC 1638 (CanLII)
School District No. 44 (North Vancouver) v. Jubran, 2005 BCCA 201 (CanLII)
Independent School Authority v Parent, 2022 BCSC 570 (CanLII)
Board of Education of School District No 43 (Re), 2013 BCIPC 20 (CanLII)
British Columbia (Education) (Re), 2018 BCIPC 2 (CanLII)
Sollitt v. Trillium Lakelands District School Board, 2013 HRTO 1128 (CanLII)
The Student v. The School District and others, 2019 BCHRT 217 (CanLII)
Steele v. School District No. 36, 2014 BCHRT 276 (CanLII)
Aslin v Edmonton Catholic Schools, 2021 AHRC 186 (CanLII),
MacKenzie v. Howe Sound School Dist. No. 48 (No. 2), 1997 CanLII 24743 (BC SC)
SJ v Parkland School Division No 70, 2019 ABQB 470 (CanLII)
Gould v. Regina (East) School Division No. 77, 1996 CanLII 6807 (SK QB)
Tsai and Tsai v. B.C. (Ministry of Education) and another, 2004 BCHRT 386 (CanLII)
Kelly v. UBC (No. 3), 2012 BCHRT 32 (CanLII)
L.B. v Toronto District School Board et al., 2017 ONSC 2301 (CanLII
HB v. Halton District School Board, 2018 HRTO 1729 (CanLII)
Rezaei v. University of Northern British Columbia and another (No. 2), 2011 BCHRT 118 (CanLII)Edit”Case Decisions and Reports Connected to Education”